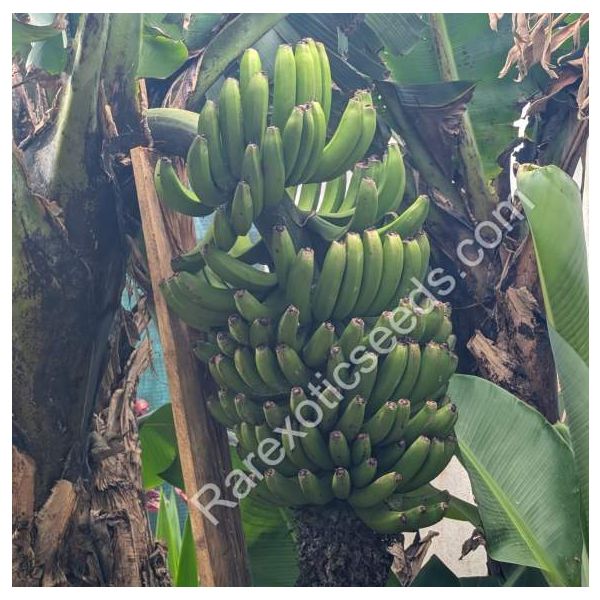
Musa × Paradisiaca Seeds (Banana Seeds)
Musa × Paradisiaca Seeds (Banana Seeds)
The fruits are sources of energy. It contains potassium, proteins, fibers, carbohydrates and an association of vitamins: A, B, B6, C and E...
Delivery
All orders shipped with UPS Express.
Always free shipping for orders over US $250.
All orders are shipped with a UPS tracking number.
Returns
Items returned within 14 days of their original shipment date in same as new condition will be eligible for a full refund or store credit.
Refunds will be charged back to the original form of payment used for purchase.
Customer is responsible for shipping charges when making returns and shipping/handling fees of original purchase is non-refundable.
All sale items are final purchases.
Help
Give us a shout if you have any other questions and/or concerns.
Email: contact@domain.com
Phone: +1 (23) 456 789
Availability: In stock
SKU
Musa x Paradisiaca
Musa Paradisiaca – Plantain Seeds
Musa paradisiaca, commonly known as the Plantain or sometimes as the Banana Plantain, is a tropical plant native to Southeast Asia and the Pacific Islands. Unlike the sweet bananas we typically consume, the plantain is starchy and commonly used for cooking in various savory dishes. Its large, lush leaves and tall stature make it a valuable addition to tropical and subtropical gardens.
Growth and Characteristics
- Height: Grows up to 15 feet (4.5 meters), creating a striking presence in your garden.
- Fruit: Produces long, starchy bananas that are typically used in cooking (fried, boiled, or baked). These fruits are larger and less sweet than regular bananas.
- Leaves: Large, broad, and glossy leaves that lend a tropical look to any landscape.
- Flowers: Small, yellow flowers appear in clusters before developing into fruit.
Cultivation and Care
- Climate: Prefers warm tropical and subtropical climates. Ideal for USDA hardiness zones 9-11 with temperatures above 60°F (15°C) year-round.
- Soil: Well-draining, rich, loamy soil that retains moisture without becoming waterlogged.
- Light: Full sun is ideal for optimal growth and fruit production, though partial shade can be tolerated.
- Watering: Regular watering is essential, especially during the growing season. Keep the soil moist, but ensure proper drainage.
- Germination: Plant seeds in well-draining soil, keeping the temperature warm. Germination may take a few weeks, so be patient and maintain consistent moisture and warmth.
Plantain Uses
Musa paradisiaca is a staple in many tropical regions, where it is used for its starchy fruit in cooking. The plantain can be prepared in a variety of ways, from savory dishes to fritters and chips. Its large leaves are also utilized for wrapping food in traditional cooking methods.
Order your Musa paradisiaca seeds today and grow your own plantains for delicious tropical meals!
#MusaParadisiaca #Plantain #TropicalFruits #CookWithPlantains #TropicalGardening #HomeGarden
| Common name | French Plantain |
|---|---|
| Family | Musaceae |
| Genus | Musa |
| Species | Musa |
| Cultivar | × Paradisiaca |
| Therapeutic uses | Unripe bananas and plantain fruits are astringent, and used to treat diarrhea. The leaves are used for cough and bronchitis. The roots can arrest hemoptysis and possess strongly astringent and anthelmintic properties. Plantain juice is used as an antidote for snakebite. Other uses are asthma, burns, diabetes, dysentery, excessive menstrual flow, fever, gangrene, gout, headache, hemorrhage, inflammation, insomnia, intestinal parasites, sores, syphilis, tuberculosis, ulcers, and warts. In Suriname's traditional medicine, the red protecting leaves of the bud was used against heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia). Other therapeutic uses were against diarrhea, dysentery, migraine, hypertension, asthma and jaundice. |
| Germination | The seeds are dormant which means that the oil / liquid chamber has dried up and they will float in water. The seeds remain viable for years. There are several methods for germination. Soak seed in warm water for 24 hours before sowing. Sow seeds 1 inch deep, in pots or trays of moist seed compost. Place in a propagator or warm place, and keep at a constant temperature of between 68-77F. After sowing, do not exclude light as this helps germination. Keep the surface of the compost moist but not waterlogged; germination can take 1 to 6 months and may be slow and erratic. When large enough to handle, transplant seedlings into 7.5cm (3 inch) pots or trays, taking care not to damage the root system. Grow on in well-lit conditions, and pot on plants as required. Seeds sown at 70-75øF (21-24øC) are slow to germinate and can take 1 week up to two years to emerge. Another method is to put them into plastic zip seal bags with growing media / vermiculite / sphagnum moss or folded coffee filter. Again one should provide warm temperatures, light and moisture (not too damp). |
| Price View | Price Range |

