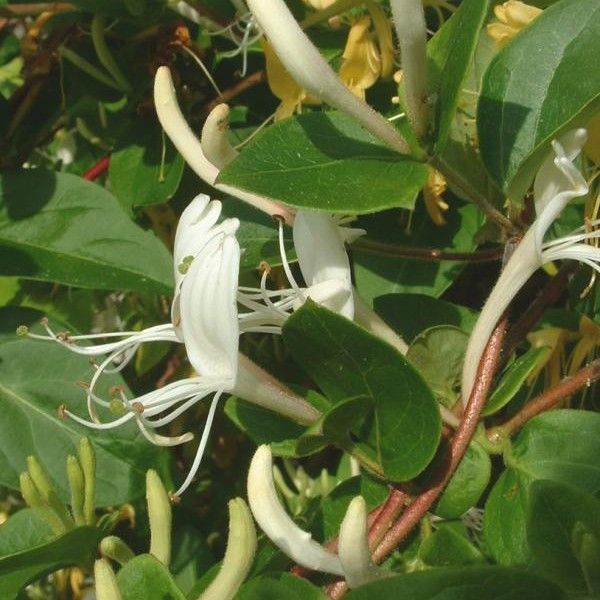
Lonicera Japonica Seeds (Japanese Honeysuckle Seeds)
Lonicera Japonica Seeds (Japanese Honeysuckle Seeds)
The stems and flower buds are alterative, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic...
Delivery
All orders shipped with UPS Express.
Always free shipping for orders over US $250.
All orders are shipped with a UPS tracking number.
Returns
Items returned within 14 days of their original shipment date in same as new condition will be eligible for a full refund or store credit.
Refunds will be charged back to the original form of payment used for purchase.
Customer is responsible for shipping charges when making returns and shipping/handling fees of original purchase is non-refundable.
All sale items are final purchases.
Help
Give us a shout if you have any other questions and/or concerns.
Email: contact@domain.com
Phone: +1 (23) 456 789
Availability: Out of stock
SKU
Lonicera Japonica
The Japanese Honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica) is a species of honeysuckle native to eastern Asia including China (northern and eastern P.R.China and Taiwan), Japan, and Korea. It is a twining vine able to climb up to 10 metres (33 ft) high or more in trees, with opposite, simple oval leaves 3?8 centimetres (1.2?3.1 in) long and 2?3 centimetres (0.79?1.2 in) broad. The flowers are double-tongued, opening white and fading to yellow, and sweetly vanilla scented. The fruit is a dark blue berry 5?8 millimetres (0.20?0.31 in) diameter containing numerous seeds.
The Japanese Honeysuckle flower is of high medicinal value in traditional Chinese medicine, where it is called r?n d?ng t‚ng (Chinese: ???; literally "winter enduring vine") or j?n y¡n hu? (Chinese: ???; literally "gold silver flower"). It has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, and is used (often in combination with Forsythia suspensa) to dispel heat and remove toxins, including carbuncles, fevers, influenza and ulcers. In Korean, it is called geumeunhwa. The dried leaves are also used in traditional Chinese medicine.
Hardiness zone: 4-9
| Common name | Japanese Honeysuckle |
|---|---|
| Family | Caprifoliaceae |
| Genus | Lonicera |
| Species | Lonicera Japonica |
| Germination | Once the Lonicera japonica seeds are stratified, plant them in a peaty soil mixture. Seeds are generally sown on the surface of the soil and covered with 1/8-inch layer of peat moss. Planting distance is unimportant at this point because the seedlings will be transplanted before they become too large and begin to crowd one another. The medium must be kept moist at all times during germination. Plastic wrap over the planting container acts like a mini-greenhouse, keeping the soil moist and the environment warm. |
| Scarification / Stratification | The seeds require cold, moist stratification to break dormancy. Envelop the seeds in a handful of moist sphagnum peat moss or sand. The bundle is then placed in a plastic bag, sealed and placed in the refrigerator for 60 days. |
| Price View | Price Range |

